The Impact of Rising Mortgage Rates
Hello there. I’m Windermere Real Estate’s Chief Economist Matthew Gardner. Welcome to the latest episode of Monday with Matthew.
Over the past several weeks I’ve gotten a lot of messages from you wanting me to discuss the spike in mortgage rates that followed comments by the Federal Reserve, but also asking me if there will be any impacts to the housing market following Russia’s invasion of the Ukraine. This is clearly a hot topic right now, so today we are going to take a look at how these events have impacted mortgage rates, but also look at how this may have changed my mortgage rate outlook for 2022. So, let’s get to it.
Weekly Mortgage Rates
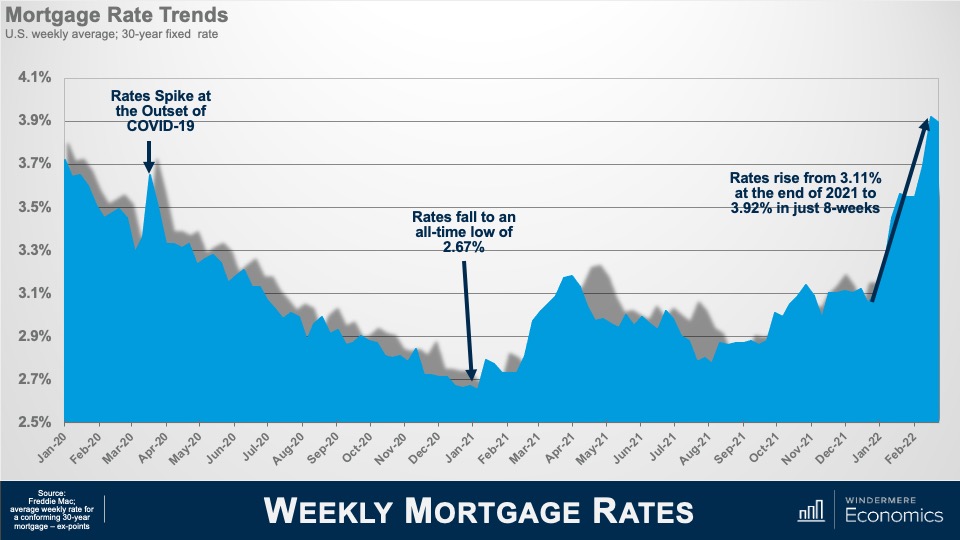
Here is a chart that shows how rates have moved over the past two years or so using Freddie Mac’s average weekly rate for a conforming 30-year mortgage. You’ll see that rates were falling in early 2020, but when COVID-19 was announced as a pandemic they spiked, but almost immediately the Fed announced their support for the economy by implementing a broad array of actions to keep credit flowing and limit the economic damage that the pandemic would likely create. And part of that support included large purchases of U.S. government and mortgage-backed securities. With the Fed as a major buyer of mortgage securities, rates dropped ending 2020 at a level never seen in the more than 50 years that the 30-year mortgage has been with us.
In early 2021, rates started to rise again as the country became more confident that the pandemic was coming under control, but all that changed with the rise the Delta variant of COVID-19 which pushed rates lower through mid-summer. As we again started to believe that COVID was under control and a booster shot became available, you’ll see rates resumed their upward trend in August.
What has everyone worried today is this spike that really took off at the end of last year. A jump of almost a full percentage point in just eight short weeks understandably has a lot of agents, buyers, and sellers, concerned about what impacts this might have on what has been a remarkably buoyant housing market. Now, rates rising so quickly was unusual, but not unprecedented. If you really wanted to be scared, I’d regale you with stories from 1980 when mortgage rates jumped by over 3.5% in less than eight weeks.
Anyway, before we really dig into this topic, some of you may be thinking to yourselves that my numbers have to be wrong because they differ from the rates you have been looking at. This is due to the fact that the Freddie Mac survey methodology is different from other rate surveys but, even though their rates may not match the ones you’ve been seeing from other data providers, the trend is still consistent.
So, let’s chat for a bit about what caused the spike in rates. You know, it’s always good to have a villain in any story and the primary but certainly not sole culprit responsible for the jump in rates is—you guessed it—the Federal Reserve.
As I mentioned earlier, the Fed was the biggest buyer of pools of home loans (otherwise known as mortgage-backed securities) as we moved through the pandemic, but last December they announced an end to what had been an era of easy money by winding down these purchases in order to lay the groundwork for shrinking their 2.7 trillion—yes I said “trillion”—dollar stockpile of MBS paper they had built up. This decision to move from “quantitative easing” to “quantitative tightening” so rapidly had an almost immediate impact on mortgage rates simply because the market was going to lose its biggest buyer of mortgage bonds.
Immediately on the heels of their announcement, bond sellers raised the interest rate on their bond offerings to try and find buyers other than the Fed, so lenders raised the rates on mortgages housed within these bond offerings. Finally, mortgage brokers moved quickly to raise the rates that they were quoting to the public. The result of all this was that rates leapt. Although we know that the primary party responsible for rates rising was the Fed, there were other players too, and here I am talking about inflation—and as you are no doubt aware—it too started to spike at the beginning of this year and now stands at a level not seen since 1982. And if you’re wondering why inflation is important. Well, high inflation is a disincentive to bond buyers because if the rate of return, or interest on mortgage bonds, is lower than inflation, investors lose interest pretty quickly.
So, we can blame the Fed, we can blame inflation, but what about Russia? Well, their invasion of the Ukraine on February 24 has certainly influenced mortgage rates, but maybe not in the way you might expect. In general, when there’s any sort of global or national geopolitical event, investors tend to gravitate to safety, and this invariably means a shift out of equities and into bonds.
So you would be correct is thinking that at face value Russia was actually responsible for the tiny drop in rates we saw following the invasion, and also the more significant drop we saw last week when the market saw the biggest two-day drop in rates in over a decade. But before you start to think that rates are headed back to where they were a year ago, I’ve got some bad news for you. That is almost guaranteed not to happen.
Given what we know today, the terrible conflict in Eastern Europe is highly unlikely to push rates back down to where they were at the start of this year, but they will—at least for now—act as a headwind to rates continuing to head higher at the pace we have seen over recent weeks. That will continue until the conflict is hopefully peaceably concluded. And although the Ukraine situation is unlikely to have any significant impact up or down on mortgage rates, there are some indirect impacts which could negatively hit the housing market. Now I’m talking about oil.
Russia is the third largest energy producer in the world and an already tight global oil supply could get even tighter following newly announced financial sanctions on Russia. A barrel of oil has jumped by almost $20 to $109 a barrel since the start of the occupation and, if the occupation is sustained, and Russia is faced with even greater sanctions, I wouldn’t be surprised to see the price of gas rise by between 20 and 40 cents a gallon. And it’s this, in concert with already high inflation, which will directly hit consumers wallets and this itself could certainly impact mortgage borrowing. So we can blame the Fed, we can blame inflation and we can blame Russia for the jump in rates, but are the rates you are seeing today really something to lose sleep over? I actually don’t think so. At least not yet.
Even with mortgage rates where they are today, I look at them and think to myself that they are still exceptionally low by historic standards and that there really is no need for panic. But let me explain my thinking to you. To do this, we will take a look at the impact of rising mortgage rates, not as it relates to buyers’ ability to finance a home purchase, but on how it impacts their monthly payments.
Hypothetical Home Purchase

For this example, we’ll use the peak sale price for a single-family home in America, which was just over $370,000 back in June of last year. And to finance this purchase, a buyer was lucky enough to lock in the lowest mortgage rate for that month at 2.96%. Assuming that they put 20% down, and are paying the U.S. average homeowners insurance premium and average property taxes a buyer closing on that home in June of last year would have a monthly payment of $1,682.
Now, what if a buyer had bought the exact same house but in February of this year? Well, the average rate for the third week of February was 4.06%—a big jump from last June—and higher mortgage rates would have increased their payment to $1,864. What does this all mean? Well, a jump of over a full percentage point means that the monthly payment is more, but only a relatively modest $182. So, even though rates have risen by almost a full percentage point, the increase in payments was, I think you’ll agree, relatively nominal.
But what if rates had risen to 5%? Well, that would be a very different picture with payments increasing by a far more significant $348. Of course, this is a very simplistic way of looking at it as I have not included any other debt payments that a buyer may have, but I hope that it does demonstrate that, even though mortgage rates are certainly significantly higher than they were last summer, because we started from such a low basis, monthly payments have seen a relatively modest increase. The bottom line is that rates were never going to hold at the record lows we have seen, and we need to just accept the fact that they will continue trending higher as we move through the year but are yet at a level that suggests impending doom for the housing arena. So, where do I think that rates will be by the end of this year? Well, here is my very latest forecast for the rest of this year.
Mortgage Rates Forecast
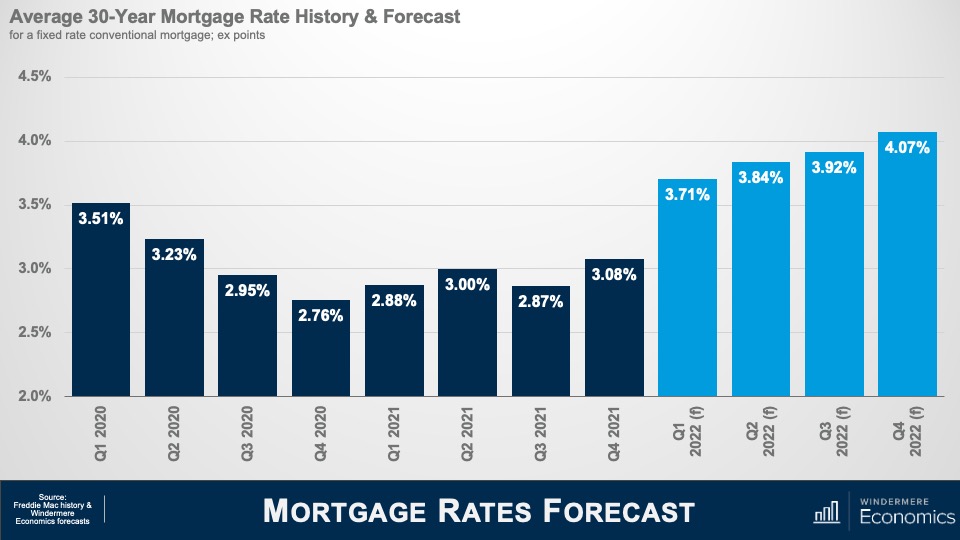
Given all we know in respect to the Fed and the current situation in Ukraine, my model suggests a significant jump in the first quarter, but then the pace of increase slows significantly and we will end this year at a rate that is almost half a percentage point above the forecast I offered at the start of the year.
Forecasts From Various Analysts
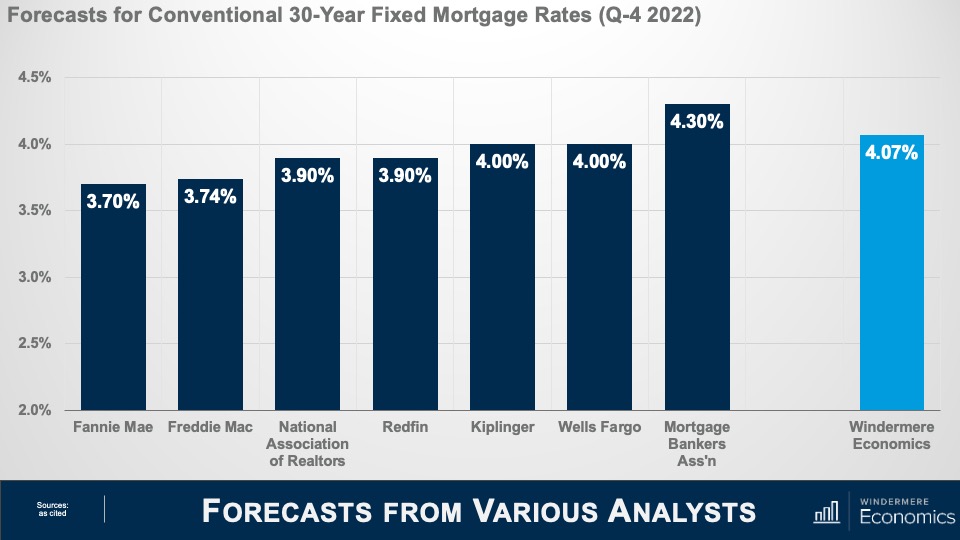
Of course, this is the opinion of just one economist, so I thought it would be useful for you to see what others are thinking. And amazingly enough, most of us—at least for now—are still in a pretty tight range regarding our expectations for the average rate in the 4th quarter of 2022 with Fannie Mae at the low end of the spectrum and the Mortgage Bankers Association at the high end.
I honestly believe that, all things being equal, the impact of higher mortgage rates is unlikely to significantly impact the U.S. market this year and, even with rates rising, the market will remain tight in terms of supply and will continue to favor home sellers. That said, once we break above 4.5%, I would expect to see the increased cost of financing having a greater impact on not just on demand but on price growth, too.
And if you are wondering why I am so sure about this, it’s simply because we saw the exact same situation in 2018 when rates rose to 4.9% and we saw a palpable pull back in sales; which dropped from an annual rate of 5.4 million to 5 million units and the pace of price growth dropped from 5.9% to 3.3%. Now, I don’t see rates getting close to 5% for quite some time and therefore still expect demand to remain robust—off the all-time highs we have seen—but still solid given demographically-driven demand as well as increasing demand from buyers trying to find a new home before rates much further.
Of course, the impact of rates rising will not be felt equally across all markets. Many areas, and especially in coastal States, have seen home values skyrocket to levels that are well above the national average. Although incomes are generally higher in these markets, buyers in more expensive areas will feel more pain from higher financing costs.
And there you have it. I hope that today’s chat has not only given you some additional tools to use in your day-to-day business but has also given you enough information to hopefully ease some of the worry that many of you are feeling right now. As always, if you have any questions or comments about this particular topic, please do reach out to me but, in the meantime, stay safe out there and I look forward to visiting with you all again next month.
Bye now.

 Facebook
Facebook
 X
X
 Pinterest
Pinterest
 Copy Link
Copy Link